Blog

Deep Learning: Unveiling the Depths of Modern AI
Dive into the transformative world of deep learning, a cornerstone of modern artificial intelligence. This comprehensive article covers the essentials of deep learning, including its architecture, featuring neurons, layers, activation functions, loss functions, and optimization algorithms. Explore advanced techniques and discover future trends that aim to enhance the interpretability, efficiency, and generalization of deep neural networks (DNNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
What is deep learning?
In the ever-evolving realm of artificial intelligence, deep learning stands as a cornerstone technology. It has revolutionized industries, enabling breakthroughs in fields ranging from healthcare to autonomous vehicles. But what exactly is deep learning, and why is it so transformative? This blog delves into the advanced concepts of deep learning, exploring its architecture, applications, and the future it promises.

What Makes Deep Learning Different? Understanding Automatic Feature Discovery with Multi-Layer Neural Networks.
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning, characterized by neural networks with many layers—hence the term "deep." Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms that rely on feature engineering, deep learning algorithms automatically discover representations needed for classification or detection from raw data. This self-discovery is made possible through the use of multi-layered neural networks, primarily deep neural networks (DNNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
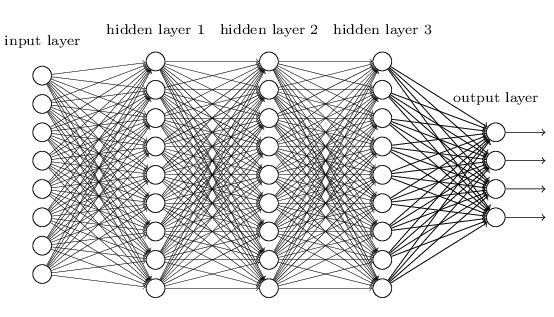
The Architecture of Deep Learning:
1. Neurons and Layers
- Input Layer: This layer receives the raw input data.
- Hidden Layers: Multiple layers that perform transformations on the input data. Each layer's output is the input to the next.
- Output Layer: This layer produces the final prediction or classification.
2. Activation Functions
Activation functions introduce nonlinearities into the network, allowing it to learn complex patterns. Common activation functions include:
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit): Introduces non-linearity by outputting the input directly if it is positive, otherwise, it outputs zero.
- Sigmoid: Squashes the input value to a range between 0 and 1.
- Tanh (Hyperbolic Tangent function) : Squashes the input value to a range between -1 and 1.
3. Loss Functions
Loss functions measure the difference between the network's prediction and the actual target. Popular loss functions include:
- Mean Squared Error (MSE): Used for regression tasks.
- Cross-Entropy Loss: Used for classification tasks.
4. Optimization Algorithms
Optimization algorithms adjust the network's weights to minimize the loss function. The most commonly used optimizer is:
- Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD): Iteratively adjusts the weights using the gradients of the loss function.
Advanced Techniques in Deep Learning:
1. Regularization
To prevent overfitting, regularization techniques such as Dropout and L2 regularization are employed.
- Dropout: Randomly drops units (neurons) during training to prevent co-adaptation of neurons.
- L2 Regularization: Adds a penalty equal to the squared magnitude of weights to the loss function.
2. Transfer Learning
Transfer learning leverages pre-trained models on large datasets, fine-tuning them on specific tasks. This approach significantly reduces training time and improves performance on smaller datasets.
3. Attention Mechanisms
Attention mechanisms allow the model to focus on relevant parts of the input sequence, improving performance in tasks like machine translation and image captioning.
4. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs consist of two neural networks—the generator and the discriminator—that compete against each other, resulting in the generation of highly realistic data.
Applications of Deep Learning
1. Healthcare
- Medical Imaging: Deep learning models can detect diseases from medical images with high accuracy.
- Drug Discovery: Predicts molecular behavior and accelerates the discovery of new drugs.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
- Object Detection: Identifies objects on the road, such as pedestrians and other vehicles.
- Path Planning: Determines the optimal path for the vehicle to follow.
3. Explainability al Language Processing (NLP)
- Language Translation: Translates text from one language to another with high accuracy.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyzes the sentiment of text data, useful for customer feedback analysis.
4. Finance
- Algorithmic Trading: Uses deep learning to predict stock prices and make trading decisions.
- Fraud Detection: Identifies fraudulent transactions by learning patterns in transactional data.
The Future of Advanced Neural Networks: Enhancing Interpretability, Efficiency, and Generalization
The future of deep learning holds immense promise with ongoing research focusing on:
- Making deep learning models more interpretable and transparent.
- Efficiency: Reducing the computational power and data required to train deep learning models.
- Generalization: Developing models that can generalize well across different tasks and domains.
Deep learning is a transformative technology, pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve. Its advanced architectures and techniques enable solutions to complex problems, making significant impacts across various industries. As research progresses, the capabilities of deep learning will continue to expand, ushering in a new era of innovation and possibilities.


